Decolorization for refined syrup
Abstract: decolorization and cross-pollination are the key processes of sugar purification in the production of starch sugar and the basis of producing high-quality products. This paper introduces the application of granular activated carbon adsorption and regeneration device in the production of starch sugar, and the subsequent automatic ion exchange system to realize the deep purification of sugar solution, at the same time, the product quality is improved and the cost is reduced.
1 preface
The technology of crystal glucose production has been quite mature, but up to now, there are still some problems such as unstable filtration rate, low whiteness of filter membrane, excessive bacteria or bacterial endotoxin. The key to solve these problems is the purification of the syrup before crystallization, while the requirements of syrup production such as fructose and maltose are much higher.
Activated carbon decolorization and Ion-exchange resin desalination are the most common and reliable means of purifying sugar solutions in starch sugar production.
Although the glucose content of the syrup obtained from the liquefaction and saccharification of starch meets the requirements, it still contains various unfavorable impurities, such as: large molecular weight color-based compounds, proteins, small molecular weight/polar color-based compounds, odor and smell compounds, as well as hydroxymethylglyoxal and so on. These impurities can be used activated carbon porous structure characteristics of adsorption removal, in the industry known as“Decolorization.”.
To date, two types of activated carbon products have been widely used in the decolorization of starch hydrolyzed syrups. One type is powdered carbon, which is generally used in a one-off manner (i.e. discarded or incinerated after reaching saturation) , the other is granular activated carbon, which can be recycled after several times. With the state vigorously advocating energy saving and emission reduction, developing circular economy and creating green industry, the application of decolorization and regeneration technology of granular activated carbon, which can be regenerated and reused many times and does not produce secondary pollutants, is the development trend of the industry. Practice has proved that a lot of quality and cost advantages.
1. The design and operation of granular activated carbon adsorption decolorization device
1.1 determination of design parameters
A two-step process is usually used to determine the design parameters of an adsorption device, starting with a “Sorption isotherm” determination of the selected granular activated carbon, one or several samples of carbon with the highest adsorption capacity to the target adsorbent were selected, and then the selected carbon samples were tested by pilot-scale continuous operation of adsorption column to determine the best activated carbon varieties and obtain the main parameters for design, at the same time, the operation cost is estimated.
1.2 granular activated carbon adsorbent for decolorization of starch hydrolyzed syrup
Because the starch hydrolysis syrup is a kind of viscous liquid containing certain concentration of fine suspended solid particles and partial acidity, the variation of bed resistance must be fully considered in the design of adsorbent, it also takes into account the need for regeneration of saturated carbon and the operating load of subsequent syrups (such as Ion-exchange resin and filter presses) . A well-designed carbon adsorption decolorization unit should meet the following operational requirements:
-
less equipment investment
-
less operation difficulty
-
continuous process without frequent material switching
-
full automatic control, the system has high operational reliability
-
small area
-
no waste and secondary pollution, high resource recovery rate, in line with the requirements of environmental protection and circular economy
-
cleaner production
-
as low as possible operation cost, and
-
high energy consumption, and
-
the operating load of the subsequent ion exchange system can be reduced, and the service life of the resin can be increased.
The granular activated carbon adsorption column for decolorization of starch hydrolysis syrup, designed and manufactured, has the following main features and can fully meet the above-mentioned operational requirements:
-
the design scheme of moving bed/pulsating bed continuous adsorption technology;
-
the“Upward flow” design is adopted to avoid the“Groove flow” and“Rapid gravity flow” of syrup in the adsorber, which can lead to the“Transient penetration” phenomenon, at the same time, the suspension in the syrup can be avoided from accumulating in the activated carbon bed and causing the increase of the bed resistance, the capacity of the adsorber and the decolorization efficiency are affected
-
considering the fluid property of the starch hydrolyzed syrup, adding the corresponding countermeasure design in the unit system completely eliminates the common faults of the adsorber during the operation of loading and unloading the activated carbon;
-
the system of process water recovery and reuse is designed, which can effectively reduce the process water consumption and the running load of the wastewater treatment plant. Fig. 1 is a practical picture of the installation and operation of a carbon adsorber for starch hydrolysis syrup decolorization.


圖1:尚鼎爐業科技(揚州)有限公司承建的高果糖漿GAC脈動床脫色裝置實例照片
2. On-site regeneration and recycling of decolorized activated carbon
Activated carbon adsorption technology is a common and cost-effective method, which can enable many industries to meet the limits of emission regulations, at the same time, it can also meet the requirements of many industries in product purification processing. With the rising price of newly-made activated carbon products in recent years, the new“Green” technology solution of using regenerated carbon to replace the newly made carbon for the above environmental protection or purification process has attracted the attention of relevant industry departments. Regenerated carbon is a kind of activated carbon which is used again after high temperature regeneration of saturated adsorbed carbon. Generally speaking, the purchase price of renewable carbon than the new system of activated carbon 20% to 40% , so recycling renewable carbon can significantly reduce the operating costs of users.
In addition, since the use of renewable carbon can also reduce the amount of industrial waste (waste activated carbon) treatment, users no longer have to pay for industrial waste and waste carbon-related costs, but also further reduce the operating costs of users. In fact, the technology of regenerated carbon reuse has been regarded as a renewable resource and an effective measure of cleaner production, which has a significant“Green” advantage, the utility model is an“Environment-friendly” practical technical method.
2.1 thermal regeneration of granular activated carbon
There are two types of activated carbon regeneration, thermal regeneration and chemical regeneration, and thermal regeneration is the most common method in industrial production. The thermal regeneration of saturated carbon consists of three continuous processes:
-
drying stage. Generally, the operating temperature of the regeneration furnace should be controlled at 100 something 300 ° C, so that the moisture in the saturated carbon can be forced to evaporate
-
roasting stage. The temperature control range is 400 ° 600 ° C, the organic matter adsorbed in the activated carbon micropores is evaporated and/or carbonized,
-
reactivation stage. The temperature of the furnace is controlled at 800 something 1000 ° C, and at the same time, the quantitative water vapor is introduced, so that the pores of activated carbon can be completely“Clean” and restore adsorption capacity.
There are two types of equipment systems which can meet the technical requirements of thermal regeneration, one is the rotary kiln charcoal regeneration system, the other is the multi-stage furnace regeneration system. The former is prone to“Burning carbon”(the“Skeleton carbon” of the activated carbon is burned away, thus changing the pore size and adsorption properties) , therefore, this type of equipment is not often used in the newly-built activated carbon regeneration plant, and is replaced by the multi-stage furnace regeneration equipment system.
2.2 multi-stage furnace regeneration treatment plant system for saturated activated carbon
2.2.1 the structure, Operation Characteristics and application scope of the multi-stage furnace device
The Multiple Hearth Furnace is also called Multiple Hearth Furnace. It consists of several up to a dozen circular beds stacked in parallel in the horizontal direction, all of which are self-supporting and fixed in a cylindrical shell rolled from ordinary steel plates, lined with Refractory. From the top of the furnace to receive the feed of solid raw materials, the solid material is rotated from outside to inside of the hearth (and from inside to outside of the lower hearth) by the stirring teeth (Harrow Teeth) installed on the stirring arm (Harrow Arm) of the low rotating speed (0.5 something 3rpm) center shaft, and is discharged into the next hearth, and finally from the bottom of the hearth discharge. The central shaft, the rake arm and the rake teeth are supplied with air and forced cooling by a special cooling fan. The appearance and section view of the multi-stage furnace are shown in Figure 2.
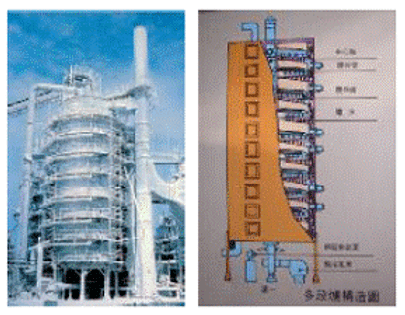
圖2 多段爐的外觀照片和剖視示意圖
The multi-stage furnace system makes gas and solid pass through a series of furnace bed structures in the form of overall countercurrent contact through the heat transfer process (the heat transfer between the external fuel combustion flue gas and the hot flue gas produced by the reaction and the solid material) The gas on each layer of the bed is cross-flow, counter-flow in the wrinkled thin layer of solid material flow and diffusion to the solid material's inner surface, these thin layers of solid materials are periodically stirred by a stirring mechanism consisting of a central shaft, a harrow arm and a Harrow tooth to keep the solids mixing and spreading and to force them into the lower hearth to continue the reaction, until the set reaction time is reached.
Multi-stage furnace system generally consists of the following core units:
-
quantitative feeding device directly connected with the multi-stage furnace, including screw feeder, air-tight feeding device.
-
multi-stage furnace body, these include: Furnace Tube, refractory lining, refractory self-supporting hearth structure and blanking hole, tail gas outlet piping (with Refractory lining) , central shaft, rake arm, rake teeth and drive unit, burner and supply of gas (or oil) and combustion-supporting air and automatic control valve-piping system, sensors and instrumentation for on-line process parameter detection system, discharge and product product forced cooling device, etc. .
-
rear combustion chamber, it includes: the structure of combustion chamber, the supply of gas (or fuel oil) and combustion air, the automatic control valve-pipeline system, the automatic control system of emergency evacuation, the sensors and instruments for on-line testing of process parameters, etc. .
-
waste heat recovery and flue gas pollutant emission control system, including waste heat recovery steam boiler, flue gas cleaning and purification device, etc. .
The main application fields of multistage furnaces are: pyrolysis/gasification or incineration of industrial and/or domestic sludge; Carbonization (roasting) and/or steam activation in the production of activated carbon, thermal regeneration of activated carbon, roasting and calcination of concentrate, and roasting and calcination of metallurgical by-products; Roasting and calcining of carbonate of magnesium, calcium and manganese, and roasting and calcining of phosphate, kaolin, sulfate, molybdate, dolomite, etc. Biomass alternative energy products such as roasting process.
2.2.2 advantages of multi-stage furnace for activated carbon regeneration treatment
When the multi-stage furnace is used for the regeneration of saturated carbon, it has the following incomparable advantages:
-
the technical parameters of regeneration can be strictly controlled, this is particularly true in the control of the atmosphere of the furnace, the ratio of steam to gas,
-
the rate of carbon loss resulting from gasification, which is generally in the range of 3% to 5% , can be reduced, lower carbon loss rate than other types of regeneration furnace (typically in the 5% to 10% range) ;
-
lower carbon loss rate due to mechanical wear;
-
lower energy consumption per unit product; Usually in the range of 2500.4500 BTU/lb of regenerated carbon (5.81-10.46 MJ/kg) ,
-
the contact rate between solid activated carbon and gas activated agent is high (the reaction rate is fast) , therefore, the minimum design capacity ratio of the furnace can be reduced to the level of 35% , and the device system is more compact;
-
the structure is simple, firm, the service life is long, the maintenance is easy;
-
the operation is simple, it is most suitable for automation and easy management;
-
the unit system occupies a small area;
-
the tail gas treatment technical system, such as the after burner, the waste heat recovery steam boiler and the flue gas scrubber, is designed, the surplus superheated steam (about 2/3 of the total steam output) can also be used in other industrial processes.
-
a process water recovery system is provided, water reuse rate can reach more than 95% ; (11) good stability to load fluctuation.
2.2.3 the structural features of the multi-stage furnace system for syrup decolorization carbon regeneration made in Shangding
After a series of technological innovation and industrialization practice, compared with the main competitors, the multi-stage furnace system for the regeneration of decolorization activated carbon of starch hydrolyzed syrup made by Shangding company has formed the following three unique technologies:
-
First, the“Self-supporting force” and“Elasticity of thermal stress adaptation” of the hearth structure can be greatly improved by using the special-shaped firebrick masonry hearth, the utility model effectively eliminates the probability of the furnace bed collapse accident caused by the severe“Thermal shock”.
-
Second, the rear combustion chamber, the waste heat recovery device and the flue gas purification unit device are used as the standard configuration units of the multi-stage furnace device system, to minimize the emission concentration and total amount of gaseous pollutants such as CO, HC, SOx, NOx and PM (2.5 or 10) generated during activated carbon regeneration, in order to meet the emission limit requirements of the increasingly stringent environmental protection regulations in the user's area, and possibly in the future, so that users can avoid the environmental problems that may be caused to them.
-
Third, the remote control interface of the multi-stage furnace system has been completely“Chinese”, which reduces the basic skill requirements of the equipment operators (which can reduce the English level requirements of the operators) , improved Operability and simplicity of automated control systems.
At present, the multi-stage furnace for syrup decolorization and carbon regeneration has been adopted by domestic large-scale starch hydrolysis syrup production enterprises. Fig. 3 is the site photo of the activated carbon regenerator installed by a domestic user enterprise, figure 4 shows the integrated process flow diagram of the starch hydrolysis syrup decolorization carbon adsorption plant and the saturated carbon regeneration plant technology system adopted by Yangzhou Technology Co. , Ltd. .

圖3 尚鼎製造的糖漿脫色炭再生多段爐裝置系統現場安裝照片

圖4 澱粉水解糖漿脫色用炭吸附裝置及飽和炭再生多段爐裝置系統工藝流程示意圖
3. Application example of granular activated carbon decolorization and regeneration system in starch sugar production
Taking a sugar liquid purification process with an annual output of 450,000 tons of crystallized glucose as an example, the matching design and operation of the decolorization and regeneration unit of granular activated carbon are illustrated:
Determination of adsorption column:
The design parameters were obtained by testing the isothermal curve of sugar solution decolorization with a pilot-scale device of granular activated carbon. The adsorption saturation period of activated carbon was about 40 days at a flow rate of 0.5 bv. When the designed flow rate was 170m3/h, the volume of online activated carbon was 1700.5 = 340m3 and the decolorization volume was 400m3. In order to ensure stable production, divided into four pulse bed decolorization column, each 100m3.
3.2 determination of the regeneration furnace:
The regeneration capacity of activated carbon = 400m 3 × 0.5 t/m 340 days = 5 t/d a regeneration system with an annual regeneration capacity of 1800 T/d is set up.
3.3 resolution of discharge membrane whiteness:
After the actual operation of the system, only 4 tons/day of activated carbon regeneration can reach the color value of decolorization discharge less than 10 RBU standard. But the pulse bed adsorption column because in the process of loading and unloading carbon friction generated by the activated carbon and the release of a small amount of powdered activated carbon, was carried to the feed liquid. This material may contaminate the later process-ion exchange resin. 1000ml of this material is filtered through a φ20mm microporous membrane, which turns dark grey and the whiteness is less than 40. Using closed plate filter, each square plate pre-coated with 1 kg of powdered activated carbon after filtering carbon column discharge, can make the material of the filter membrane whiteness of 70 or more. The airtight plate type according to 400L/m2, the filtering capacity of the design, multi-use a device, the use period is generally a week.
3.4 comparison of operation effect and economic benefit
Since the equipment has been running for nearly one year, it has achieved the set target very well. In addition to the decolorization, other impurities such as protein have been completely adsorbed and removed, this reduces the burden on the operation of the ISEP continuous demineralization system. Because the sugar liquid is well purified, the unitary material inhibits the growth of microorganisms, and without any preservative, the crystallization process does not produce the phenomenon of bacteria fermentation, the bacterial endotoxin index was less than 0.125 eu/ml.
Under normal circumstances, the natural gas consumption per ton of recycled granular activated carbon is 150 cubic meters, activated carbon loss of 3% , that is, 30 kg. Compared with the traditional process, there are obvious cost advantages, the following is the contrast:
3.4.1 comparison of direct costs
Capacity
Compare with carbon
A 450,000-ton crystallized glucose production line in China
Decolorization process of granular carbon
Decolorization process of powdered carbon
Powder carbon consumption (kg/t sugar)
Granular carbon consumption (kg/t sugar)
Natural gas consumption per unit (m3/ton sugar)
Post personnel (person)
Granular carbon price (yuan/ton)
Natural gas price (yuan/cubic)
Powder carbon price (yuan/ton)
Labor cost (yuan/ton)
Ton sugar decolorization cost (yuan/ton sugar)
Annual decolorization cost (yuan/year)
0.1
0.15
0.5
6
31000
3
8000
0.5
7.45
3,352,500
3.5
0
0
18
8000
1.5
29.5
13.275 million
Annual cost difference (yuan/year)
9,922,500
Note: since the electricity and steam consumption of the two processes are basically the same, they are not included in this table for comparison.
3.4.2 cleaner production to reduce leakage and sugar loss from waste carbon
When the granular carbon is regenerated, the“Sugar washing” operation is carried out by using high-temperature RO water to pass into an airtight decarbonization tank. The valuable sugar liquid can be recovered, and the airtight equipment prevents the occurrence of leakage and leakage, very little loss of glucose solution. The main product yield is 0.2% ~ 1% affected by the leakage and the sugar carried away by waste carbon. According to the reduction of 0.2% yield, the sugar price is 3500 yuan per ton, with an annual production capacity of 450,000 tons, the annual loss of waste carbon entrainment and plate and frame leakage: 45 * 3500 * 0.2% = 3.15 million yuan.
3.4.3 reduce the off-load, reduce the consumption of acid and alkali and reduce the cost of wastewater treatment
The separation system is the last refining process before entering the crystallizer. The carbon decolorization process can remove the colored substance stably and uniformly, which can reduce the separation load effectively The total COD of wastewater from conventional decolorization process and separation is 90% of the total COD of wastewater from Sugar Workshop. Compared with the plate-frame decolorization and the conventional up-flow fixed-bed separation, the COD emission is 2.9 times of that of granular carbon and automatic separation. There is a difference of 2 m3/t of water consumption (production data) between the two types of process, and the cost of wastewater treatment is 5 yuan/T. With an annual output of 450,000 tons, the consumption of a ton of sugar water varies by 2 m3/t. The annual additional cost of wastewater treatment is 45 * 2 * 5 = 4.5 million yuan
The cost savings compared with conventional decolorization and ion exchange after application of the new process are calculated as follows:
992.25 315 450= 17,5725 million yuan/year. In this way, the decolorization and separation process configuration of the new starch sugar factory select the combination configuration of granular carbon decolorization and automated separation system is the advanced configuration method in the industry, in line with the advocacy of circular economy, and the key can bring low cost, good quality and uniform qualified products to the owner.
4. Conclusion
With the improvement of our economic strength and people's living standard, the production and consumption of starch hydrolysis syrup is expected to be the first in the world in 2020, reaching 15 million tons per year.
Activated carbon adsorption decolorization technology is the most mature and cost-effective technology to decolorize starch hydrolyzed syrup, remove off-flavor and off-smell compounds, at the same time retain the flavor of syrup. Compared with the traditional wood-based powdered activated carbon, the coal-based acid pickling granular activated carbon product has abundant raw materials, can be regenerated repeatedly and reused, and has stable physical and chemical properties, it is a kind of“Environment-friendly” decolorization activated carbon, which can meet the requirements of starch syrup industry. The decolorization and refining of starch hydrolyzed syrup by the system of granular activated carbon adsorption decolorization-saturated carbon regeneration + automatic separation is the most popular technology route with the lowest running cost and the most stable product quality. The pulsatile-bed/fixed-bed syrup decolorization device of granular activated carbon and the multi-stage furnace system of fully automatic carbon regeneration designed by“Up-flow” are the best combination of decolorization equipment with the best performance-price ratio.
References
(Condelang. Integrated system of activated carbon refining and multi-stage furnace activated carbon refining and multi-stage furnace activated carbon regeneration treatment for starch hydrolyzed syrups. Fermentation industry, No. 3,2012. pp. 27-32.
