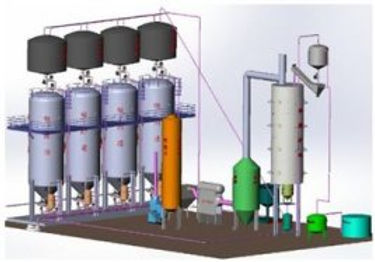
Reactivation and regeneration of granular activated carbon(GAC)
Activated carbon regeneration technology: thermal regeneration is the most widely used and the most mature industrial method of granular activated carbon regeneration. The thermal regeneration method has the characteristics of high regeneration efficiency and wide application range, but the attention should be paid to the selection of appropriate, stable operation and good “Cost/benefit” regeneration equipment system, it is the key to ensure the performance of regenerated carbon. Investors should consider energy cost, investment and operation cost, yield of activated carbon, energy saving and environmental protection, etc.
Regardless of the technical application, our regeneration system will include the following core components:
-
The quantitative feeding device directly connected with the Multiple Hearth Furnace, the utility model comprises a screw feeder, an air-tight feeding device, etc.
-
Multiple Hearth Furnace body, these include: Furnace Tube, refractory lining, refractory self-supporting hearth structure and blanking hole, tail gas outlet piping (with Refractory lining) , central shaft, rake arm, rake teeth and drive unit, burner and supply of gas (or oil) and combustion-supporting air and automatic control valve-piping system, sensors and instrumentation for on-line process parameter detection system, discharge and product forced cooling device, etc.
-
After burner chamber, it includes: the structure of combustion chamber, the supply of gas (or fuel oil) and combustion air, the automatic control valve-pipeline system, the automatic control system of emergency evacuation, the sensors and instruments for on-line testing of process parameters, etc.
-
Waste heat recovery and flue gas pollutant emission control system, including waste heat recovery steam boiler, flue gas scrubbing and purifying device, etc.
After the saturated carbon is washed in the discharge chute of the activated carbon thermal regeneration process (Multiple Hearth Furnace system) , a pressurized water is introduced to form a“ Carbon slurry” which is pumped to the Furnace Feed Tank of the regeneration Furnace, saturated carbon is fed by a Dewatering Screw Feeder and “Reactivated” by adding a Multiple Hearth regeneration Furnace.
The structure of the Multiple Hearth Furnace shows that the inner lining refractory layer of the steel plate cylindrical furnace body is built with special firebrick to build the furnace bed with “Self-supporting” structure, and the furnace is divided into several sections, each section of the hearth is respectively provided with a plurality of “Blanking holes” at the periphery or near the center of the hearth, materials are alternately “Stirred” and moved from the outside to the inside of the hearth (“Inner rake” operation) by the rake arm mounted on the low-speed (0.5-3rpm) central shaft and by groups of rake teeth mounted on the rake arm, and from the inside to the outside of the adjacent next hearth (“Outer rake” operation) , the solid material is in convective contact with the gaseous product at the blanking hole. The hollow shaft in the center of the furnace and the hollow rake arm installed on the shaft are fed into the cold air by a special shaft cooling fan for continuous forced cooling operation. The schematic diagram of the Multiple Hearth Furnace is as follows:


Granular activated carbon regeneration method of Multiple Hearth Furnace belongs to thermal regeneration, it consists of the following three stages:
1) DRYING stage: evaporation and drying of activated carbon at 100-300 °C in stages 1 and 2 of a six-stage furnace.
2) BAKING stage: in the third stage of the six-stage furnace, the volatiles of the organic matter were evaporated and charred from the pores of adsorbed activated carbon at 400-600 °C.
3) ACTIVATION stage: in the 4th-6th stage of the 6-stage furnace, steam is introduced at a high temperature of 800-1000 ° C to make the “Residual carbon” remaining in the pore structure of activated carbon after the carbonization of organic matter in the drying stage occurs a gasification reaction: C + H2O → CO + H2, and is “Cleared”, the pore structure and inner surface of the activated carbon are “Cleaned”, and the adsorption and decolorization performance of the activated carbon is restored to a level similar to new carbon. A quench tank is arranged below the Multiple Hearth Furnace to make the activated carbon quench and degassing. It is then fed to the CARBON CHARGED TANK by a dedicated EJECTOR unit and waits for the next PULSE operation.
Since the Multiple Hearth Furnace is required to operate in an atmosphere with an oxygen concentration of not more than 1% (with the aim of reducing the regeneration loss rate of activated carbon) to selectively remove impurities such as organic matter and colloid adsorbed in activated carbon micropores, in the reactivation reaction C + H2O → CO + H2, CO and H2 combustible gases are formed, and the low-molecular-weight combustible organic matter volatilized from saturated carbon in the baking stage must be treated to meet the emission requirements. The after burner furnace arranged in the Multiple Hearth Furnace system can make the above-mentioned combustibles completely combust with the combustion-supporting air at the operating temperature above 750 °C, and finally be transformed into carbon dioxide and water vapor; The waste heat recovery of high-temperature flue gas from combustion process can not only be used for self-activation, but also for other processes, pollutants such as low concentration sulfides and dust in the flue gas are removed in the gas washer impingement-scrubber. The final emission of flue gas can fully meet the requirements of environmental regulations.
In the process of process water reuse system, saturated carbon, regenerated carbon and supplemental new carbon are transported by hydraulic technology. In order to save water resources, a process water recovery system is specially set up in the process. The overflow water of the quench and the carbon high position tank is introduced into the recovery water tank through the overflow water tank and used as the process water of the activated carbon conveying system.